Search results
A tuning fork is an acoustic resonator in the form of a two-pronged fork with the prongs (tines) formed from a U-shaped bar of elastic metal (usually ... more
BHN or Brinell Number is the numerical value assigned to the hardness of metals and alloys. The test is to determine the hardness ... more
A porous medium (or a porous material) is a material containing pores (voids). The skeletal portion of the material is often called the ... more
The selection of synthetic membranes for a targeted separation process is usually based on few requirements. Membranes have to provide enough mass transfer ... more
In physics, the gyromagnetic ratio (also sometimes known as the magnetogyric ratio in other disciplines) of a particle or system is the ratio of its ... more
In optics, a Gaussian beam is a beam of electromagnetic radiation whose transverse electric field and intensity (irradiance) distributions are well ... more
Thermal energy is a term sometimes used to refer to the internal energy present in a system in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium by virtue of its ... more
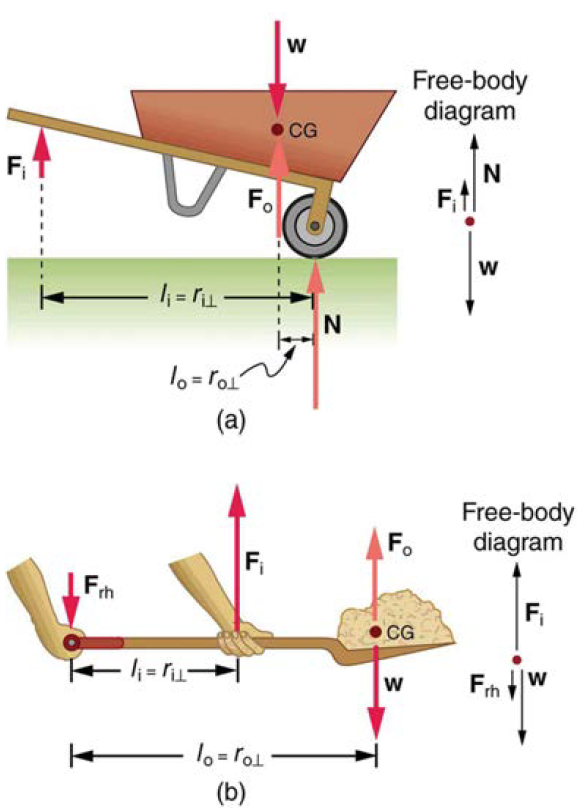
(a) In the case of the wheelbarrow, the output force or load is between the pivot and the input force. The pivot is the wheel’s axle. Here, the output force is greater than the input force. Thus, a wheelbarrow enables you to lift much heavier loads than you could with your body alone. (b) In the case of the shovel, the input force is between the pivot and the load, but the input lever arm is shorter than the output lever arm. The pivot is at the handle held by the right hand. Here, the output force (supporting the shovel’s load) is less than the input force (from the hand nearest the load), because the input is exerted closer to the pivot than is the output.
Strategy
Here, we use the concept of mechanical advantage.
Discussion
An even longer handle would reduce the force needed to lift the load. The MA here is:
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
In probability and statistics,the Cauchy distribution, is a continuous probability distribution. The simplest Cauchy distribution is called the standard ... more
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) is the volume of air present in the lungs, specifically the parenchyma tissues, at the end of ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
In the wheelbarrow of the following figure the load has a perpendicular lever arm of 7.50 cm, while the hands have a perpendicular lever arm of 1.02 m.(a) What upward force must you exert to support the wheelbarrow and its load if their combined mass is 45.0 kg? (b) What force does the wheelbarrow exert on the ground?