Search results
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the ... more
Antenna measurement techniques refers to the testing of antennas to ensure that the antenna meets specifications or simply to characterize it. Typical ... more
In probability and statistics,the Cauchy distribution, is a continuous probability distribution. The Cauchy distribution is often used in statistics as the ... more
Drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) refers to forces acting ... more
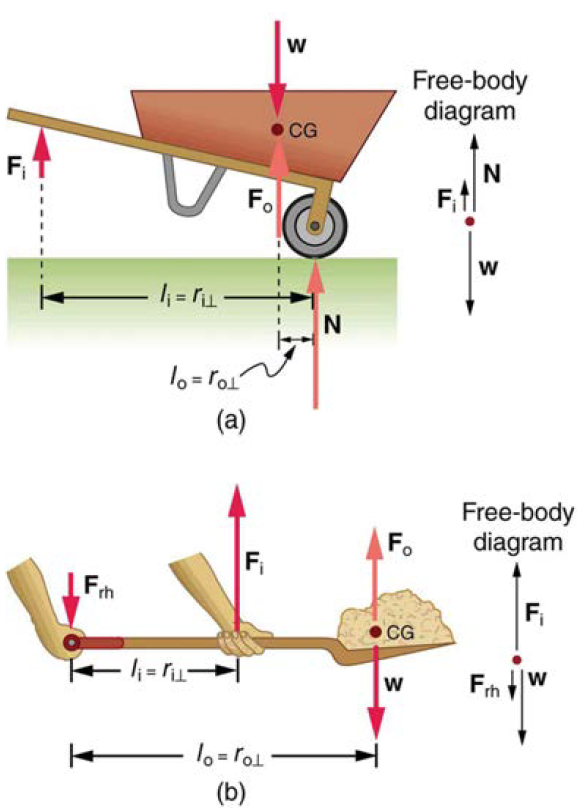
(a) In the case of the wheelbarrow, the output force or load is between the pivot and the input force. The pivot is the wheel’s axle. Here, the output force is greater than the input force. Thus, a wheelbarrow enables you to lift much heavier loads than you could with your body alone. (b) In the case of the shovel, the input force is between the pivot and the load, but the input lever arm is shorter than the output lever arm. The pivot is at the handle held by the right hand. Here, the output force (supporting the shovel’s load) is less than the input force (from the hand nearest the load), because the input is exerted closer to the pivot than is the output.
Strategy
Here, we use the concept of mechanical advantage.
Discussion
An even longer handle would reduce the force needed to lift the load. The MA here is:
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force ... more
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
Drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) refers to forces acting ... more
The surface gravity, g, of an astronomical or other object is the gravitational acceleration experienced at its surface. The surface gravity may be thought ... more
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
In the wheelbarrow of the following figure the load has a perpendicular lever arm of 7.50 cm, while the hands have a perpendicular lever arm of 1.02 m.(a) What upward force must you exert to support the wheelbarrow and its load if their combined mass is 45.0 kg? (b) What force does the wheelbarrow exert on the ground?