Search results
A spring is an elastic object used to store mechanical energy. Springs are usually made out of spring steel. Small springs can be wound from pre-hardened ... more
In lead climbing using a dynamic rope, the fall factor (f) is the ratio of the height (h) a climber falls before the climber’s rope begins to stretch ... more
Hooke’s Law of elasticity is an approximation that states that the amount by which a material body is deformed (the strain) is linearly related to ... more
When a force is applied on a spring, and the length of the spring changes by a differential amount dx, the work done is Fdx. For linear elastic springs, ... more
Hooke’s law states that the force needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance is proportional to that distance.The stresses and strains ... more
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each ... more
Hooke’s law is a principle of physics that states that the force F needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance X is proportional to that ... more
A harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force, proportional to the displacement. If a ... more
Elastic energy is the potential mechanical energy stored in the configuration of a material or physical system as work is performed to distort its volume ... more
The simple harmonic motion is a type of periodic motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement. The frequency of a simple ... more
In mechanics and physics, simple harmonic motion is a type of periodic motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement. It ... more
Surface tension is a contractive tendency of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. Surface tension is an important property ... more
Damped harmonic motion is a real oscillation, in which an object is hanging on a spring. Because of the existence of internal friction and air resistance, ... more
Damped harmonic motion is a real oscillation, in which an object is hanging on a spring. Because of the existence of internal friction and air resistance, ... more
Torsion balances, torsion pendulums and balance wheels are examples of torsional harmonic oscillators that can oscillate with a rotational motion about the ... more
Leaf spring, commonly used for the suspension in wheeled vehicles. The term is also used to refer to a bundled set of leaf springs. As the spring flexes, ... more
The stiffness of a body is a measure of the resistance offered by an elastic body to deformation. For an elastic body with a single degree of freedom (for ... more
Stress is a physical quantity that expresses the internal forces that neighboring particles of a continuous material exert on each other. Any strain ... more
The stiffness of a body is a measure of the resistance offered by an elastic body to deformation. A body have a rotational stiffness when it is in a ... more
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed.
Total energy is constant in any process. It may change in form or be transferred from one system to
... more
Formula first contributed by:
trooper
In engineering, the damping ratio is a dimensionless measure describing how ... more
Potential function for electrostatic forces between two bodies is the work required to move a charge from a point to any point in the electrostatic force ... more
Potential energy is the energy of a body or a system with respect to the position of the body or the arrangement of the particles of the system. The amount ... more
In 1954, Miles developed his version of this equation for GRMS as he was researching fatigue failure of aircraft structural ... more
The stretch ratio or extension ratio is a measure of the extensional or normal strain of a differential line element, which can be defined at either the ... more
Electric potential energy, or electrostatic potential energy, is a potential energy that results from conservative Coulomb forces and is associated with ... more
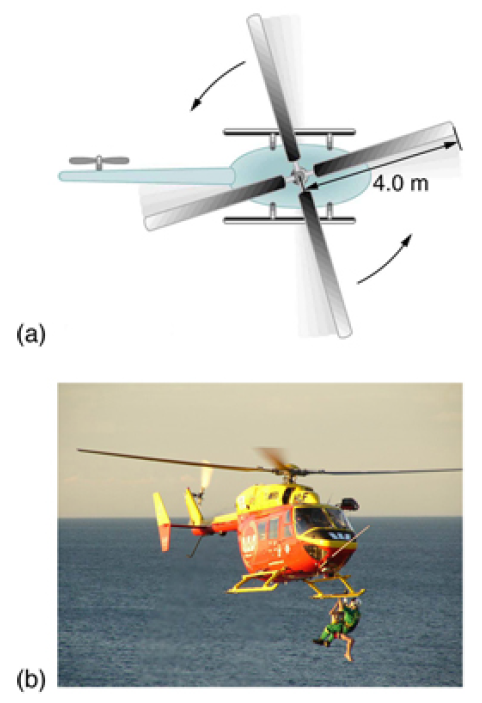
The first image shows how helicopters store large amounts of rotational kinetic energy in their blades. This energy must be put into the blades before takeoff and maintained until the end of the flight. The engines do not have enough power to simultaneously provide lift and put significant rotational energy into the blades.
The second image shows a helicopter from the Auckland Westpac Rescue Helicopter Service. Over 50,000 lives have been saved since its operations beginning in 1973. Here, a water rescue operation is shown. (credit: 111 Emergency, Flickr)
Strategy
Rotational and translational kinetic energies can be calculated from their definitions. The last part of the problem relates to the idea that energy can change form, in this case from rotational kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy.
Solution for (a)
We must convert the angular velocity to radians per second and calculate the moment of inertia before we can find Er . The angular velocity ω for 1 r.p.m is
and for 300 r.p.m
The moment of inertia of one blade will be that of a thin rod rotated about its end.
The total I is four times this moment of inertia, because there are four blades. Thus,
and so The rotational kinetic energy is
Solution for (b)
Translational kinetic energy is defined as
To compare kinetic energies, we take the ratio of translational kinetic energy to rotational kinetic energy. This ratio is
Solution for (c)
At the maximum height, all rotational kinetic energy will have been converted to gravitational energy. To find this height, we equate those two energies:
Discussion
The ratio of translational energy to rotational kinetic energy is only 0.380. This ratio tells us that most of the kinetic energy of the helicopter is in its spinning blades—something you probably would not suspect. The 53.7 m height to which the helicopter could be raised with the rotational kinetic energy is also impressive, again emphasizing the amount of rotational kinetic energy in the blades.
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
In statistical mechanics, Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics describes the average distribution of non-interacting material particles over various energy states ... more
Electrical work is the work done on a charged particle by an electric field. The equation for 'electrical’ work is equivalent to that of ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
A typical small rescue helicopter, like the one in the Figure below, has four blades, each is 4.00 m long and has a mass of 50.0 kg. The blades can be approximated as thin rods that rotate about one end of an axis perpendicular to their length. The helicopter has a total loaded mass of 1000 kg. (a) Calculate the rotational kinetic energy in the blades when they rotate at 300 rpm. (b) Calculate the translational kinetic energy of the helicopter when it flies at 20.0 m/s, and compare it with the rotational energy in the blades. (c) To what height could the helicopter be raised if all of the rotational kinetic energy could be used to lift it?