Search results
The ordinate of point of a circle, in an x–y Cartesian coordinate system, can be computed by the ordinate of the center of the circle, the radius and the ... more
The abscissa of point of a circle, in an x–y Cartesian coordinate system, can be computed by the abscissa of the center of the circle, the radius and the ... more
The abscissa of point of a circle, in an x–y Cartesian coordinate system, can be computed by the abscissa of the center of the circle, the radius and the ... more
The ordinate of point of a circle, in an x–y Cartesian coordinate system, can be computed by the ordinate of the center of the circle, the radius and the ... more
The elliptic paraboloid is shaped like an oval cup and can have a maximum or minimum point. In a suitable coordinate system with three axes x, y, and z, it ... more
In surveying, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by measuring only angles to it from known points at either end of a fixed ... more
In fluid dynamics, wave shoaling is the effect by which surface waves entering shallower water change in wave height. It is caused by the fact that the ... more
In astrodynamics an orbit equation defines the path of orbiting body around central body relative to , without specifying position as a function of time. ... more
To rotate the position of the character, we can imagine it as a point on a circle, and we will change the angle of the point by 20 degrees. To do so, we first need to find the radius of this circle and the original angle.
Drawing a right triangle inside the circle, we can find the radius using the Pythagorean Theorem:
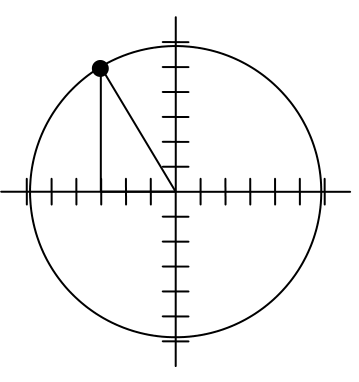
To find the angle, we need to decide first if we are going to find the acute angle of the triangle, the reference angle, or if we are going to find the angle measured in standard position. While either approach will work, in this case we will do the latter. By applying the cosine function and using our given information we get
While there are two angles that have this cosine value, the angle of 120.964 degrees is in the second quadrant as desired, so it is the angle we were looking for.
Rotating the point clockwise by 20 degrees, the angle of the point will decrease to 100.964 degrees. We can then evaluate the coordinates of the rotated point
For x axis:
For y axis:
The coordinates of the character on the rotated map will be (-1.109, 5.725)
Reference : PreCalculus: An Investigation of Functions,Edition 1.4 © 2014 David Lippman and Melonie Rasmussen
http://www.opentextbookstore.com/precalc/
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/us/
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrangian points (also Lagrange points, L-points, or libration points) are positions in an orbital configuration of two large ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
In a video game design, a map shows the location of other characters relative to the player, who is situated at the origin, and the direction they are facing. A character currently shows on the map at coordinates (-3, 5). If the player rotates counterclockwise by 20 degrees, then the objects in the map will correspondingly rotate 20 degrees clockwise. Find the new coordinates of the character.