Search results
In electronics, a vacuum tube, an electron tube, or colloquially a tube (North America) or valve (British usage), is a device that controls electric ... more
Several laws describe a human’s ability to visually detect targets on a uniform background. One such law is Riccò's law, discovered by astronomer ... more
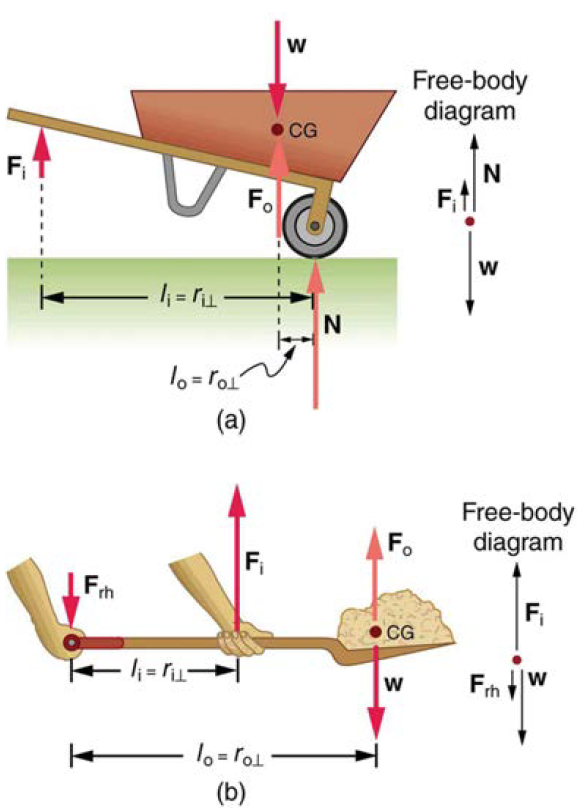
(a) In the case of the wheelbarrow, the output force or load is between the pivot and the input force. The pivot is the wheel’s axle. Here, the output force is greater than the input force. Thus, a wheelbarrow enables you to lift much heavier loads than you could with your body alone. (b) In the case of the shovel, the input force is between the pivot and the load, but the input lever arm is shorter than the output lever arm. The pivot is at the handle held by the right hand. Here, the output force (supporting the shovel’s load) is less than the input force (from the hand nearest the load), because the input is exerted closer to the pivot than is the output.
Strategy
Here, we use the concept of mechanical advantage.
Discussion
An even longer handle would reduce the force needed to lift the load. The MA here is:
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a ... more
In aerodynamics, the lift-to-drag ratio, or L/D ratio, is the amount of lift generated by a wing or vehicle, divided by the drag it creates by moving ... more
Mathematical models can project how infectious diseases progress to show the likely outcome of an epidemic and help inform public health interventions. If ... more
Discounting is a financial mechanism in which a debtor obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a ... more
A number of systems exist for the conversion of grades from other countries into German grades. One such system, used by most universities in ... more
In geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. The bearing capacity of soil is the ... more
Gravity gradiometry is the study and measurement of variations in the acceleration due to gravity. The gravity gradient is the spatial rate of change of ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
In the wheelbarrow of the following figure the load has a perpendicular lever arm of 7.50 cm, while the hands have a perpendicular lever arm of 1.02 m.(a) What upward force must you exert to support the wheelbarrow and its load if their combined mass is 45.0 kg? (b) What force does the wheelbarrow exert on the ground?