Search results
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
The Tsiolkovsky rocket equation, classical rocket equation, or ideal rocket equation is a mathematical equation that describes the motion of vehicles that ... more
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
In aerospace engineering, mass ratio is a measure of the efficiency of a rocket. It describes how much more massive the vehicle is with propellant than ... more
The Tsiolkovsky rocket equation, or ideal rocket equation describes the motion of vehicles that follow the basic principle of a rocket: a ... more
A rocket engine, or simply “rocket”, is a jet engine that uses only stored propellant mass for forming its high speed propulsive jet. Rocket ... more
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated Isp) is a measure of the efficiency of rocket and jet engines. By definition, it is the impulse delivered per unit of ... more
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated Isp) is a measure of the efficiency of rocket and jet engines. By definition, it is the impulse delivered per unit of ... more
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated Isp) is a way to describe the efficiency of rocket and jet engines. It represents the force with respect to the ... more
A rocket engine nozzle is a propelling nozzle (usually of the de Laval type) used in a rocket engine to expand and accelerate the combustion gases produced ... more
In aerospace engineering, the propellant mass fraction is the portion of a vehicle’s mass which does not reach the destination, usually used as a ... more
A water rocket is a type of model rocket using water as its reaction mass. Such a rocket is typically made from a used plastic soft drink bottle. The water ... more
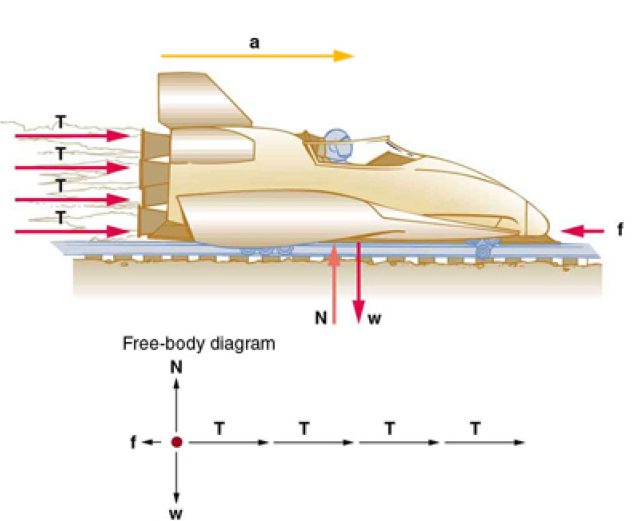
A sled experiences a rocket thrust that accelerates it to the right.Each rocket creates an identical thrust T . As in other situations where there is only horizontal acceleration, the vertical forces cancel. The ground exerts an upward force N on the system that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to its weight,w.The system here is the sled, its rockets, and rider, so none of the forces between these objects are considered. The arrow representing friction ( f ) is drawn larger than scale.
Assumptions: The mass of the Sled remains steady throughout the operation
Strategy
Although there are forces acting vertically and horizontally, we assume the vertical forces cancel since there is no vertical acceleration. This leaves us with only horizontal forces and a simpler one-dimensional problem. Directions are indicated with plus or minus signs, with right taken as the positive direction. See the free-body diagram in the figure.
Solution
Since acceleration, mass, and the force of friction are given, we start with Newton’s second law and look for ways to find the thrust of the engines. Since we have defined the direction of the force and acceleration as acting “to the right,” we need to consider only the magnitudes of these quantities in the calculations. Hence we begin with
Fnet is the net force along the horizontal direction, m is the rocket’s mass and a the acceleration.
We can see from the Figure at the top, that the engine thrusts add, while friction opposes the thrust.
Tt is the total thrust from the 4 rockets, Fnet the net force along the horizontal direction and Ff the force of friction.
Finally, since there are 4 rockets, we calculate the thrust that each one provides:
T is the individual Thrust of each engine, b is the number of rocket engines
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Characteristic velocity or c*, or C-star is a measure of the combustion performance of a rocket engine independent of nozzle performance, and is used to ... more
In astrodynamics and aerospace, a delta-v budget is an estimate of the total delta-v required for a space mission. It is calculated as the sum of the ... more
Thrust-to-weight ratio (TWR) is a dimensionless ratio of thrust to weight of a rocket, jet engine, propeller engine, or a vehicle ... more
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton’s second and third laws.
A very common question is how to contrast the thrust
... more
Thrust-to-weight ratio (TWR) is a dimensionless ratio of thrust to weight of a rocket, jet engine, propeller engine, or a vehicle ... more
The hot air balloon is the oldest successful human-carrying flight technology. The first hot-air balloon flown in the United States was launched from the ... more
Variable-mass systems, (like a rocket burning fuel and ejecting spent gases), are not closed and cannot be directly treated by making mass a function of ... more
In physics, the ballistic trajectory of a projectile is the path that a thrown or launched projectile or missile without propulsion will take under the ... more
The size of the fins controls a rocket’s stability and the amount of weather cocking (turning into the wind). The best way to determine final fin ... more
Shock diamonds (also known as Mach diamonds, Mach disks, Mach rings, doughnut tails or thrust diamonds) are a formation of standing wave patterns that ... more
A de Laval nozzle (or convergent-divergent nozzle, CD nozzle or con-di nozzle) is a tube that is pinched in the middle, making a carefully balanced, ... more
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
The nose cone section of any vehicle or body meant to travel through a compressible fluid medium (such as a rocket or aircraft, missile or bullet) is ... more
The nose cone section of any vehicle or body meant to travel through a compressible fluid medium (such as a rocket or aircraft, missile or bullet) is ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
Prior to manned space flights, rocket sleds were used to test aircraft, missile equipment, and physiological effects on human subjects at high speeds. They consisted of a platform that was mounted on one or two rails and propelled by several rockets. Calculate the magnitude of force exerted by each rocket, called its thrust T , for the four-rocket propulsion system shown in the Figure below. The sled’s initial acceleration is 49 m/s 2, the mass of the system is 2100 kg, and the force of friction opposing the motion is known to be 650 N.