Search results
In fluid flow, friction loss (or skin friction) is the loss of pressure or “head” that occurs in pipe or duct flow due to the effect of the fluid’s ... more
Electrical resistivity (also known as resistivity, specific electrical resistance, or volume resistivity) is an intrinsic property that quantifies how ... more
Surface runoff is the water flow that occurs when the soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain. The runoff curve number (also called ... more
Security characteristic line (SCL) is a regression line, plotting performance of a particular security or portfolio against that ... more
Momentum is a measure of an object tendency to move in a straight line with constant speed. Momentum has a direction and can be used to predict the ... more
Pressure vessels are held together against the gas pressure due to tensile forces within the walls of the container. The normal (tensile) stress in the ... more
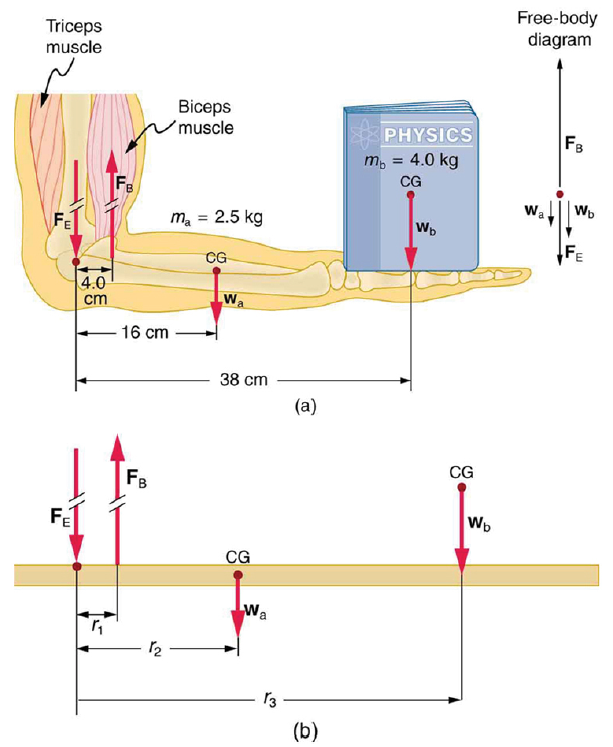
(a) The figure shows the forearm of a person holding a book. The biceps exert a force FB to support the weight of the forearm and the book. The triceps are assumed to be relaxed. (b) Here, you can view an approximately equivalent mechanical system with the pivot at the elbow joint
Strategy
There are four forces acting on the forearm and its load (the system of interest). The magnitude of the force of the biceps is FB, that of the elbow joint is FE, that of the weights of the forearm is wa , and its load is wb. Two of these are unknown FB, so that the first condition for equilibrium cannot by itself yield FB . But if we use the second condition and choose the pivot to be at the elbow, then the torque due to FE is zero, and the only unknown becomes FB .
Solution
The torques created by the weights are clockwise relative to the pivot, while the torque created by the biceps is counterclockwise; thus, the second condition for equilibrium (net τ = 0) becomes
Note that sin θ = 1 for all forces, since θ = 90º for all forces. This equation can easily be solved for FB in terms of known quantities,yielding. Entering the known values gives
which yields
Now, the combined weight of the arm and its load is known, so that the ratio of the force exerted by the biceps to the total weight is
Discussion
This means that the biceps muscle is exerting a force 7.38 times the weight supported.
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Bernoulli’s principle states that for an inviscid flow, an increase in the speed of the fluid occurs simultaneously with an increase in dynamic ... more
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated Isp) is a way to describe the efficiency of rocket and jet engines. It represents the force with respect to the ... more
Gravity gives weight to physical objects and causes them to fall toward the ground when dropped.
If Μ is a point mass or the mass of a sphere with
... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
Calculate the force the biceps muscle must exert to hold the forearm and its load as shown in the figure below, and compare this force with the weight of the forearm plus its load. You may take the data in the figure to be accurate to three significant figures.