Search results
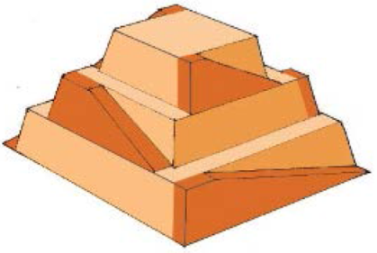
a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the pyramid, given its center of mass is at one-fourth its height.
b) Only a fraction of the workers lifted blocks; most were involved in support services such as building ramps, bringing food and water, and hauling blocks to the site. Calculate the efficiency of the workers who did the lifting, assuming there were 1000 of them and they consumed food energy at the rate of 300 Kcal/hour.
first we calculate the number of hours worked per year.
then we calculate the number of hours worked in the 20 years.
Then we calculate the energy consumed in 20 years knowing the energy consumed per hour and the total hours worked in 20 years.
The efficiency is the resulting potential energy divided by the consumed energy.
In mathematics, a magic cube is the 3-dimensional equivalent of a magic square, that is, a number of integers arranged in a n x n x n pattern such that the ... more
In recreational mathematics, a magic square is an arrangement of distinct numbers, usually integers, in a square grid, where the numbers in each row, and ... more
A geometric progression, also known as a geometric sequence, is a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous ... more
In astronomy, Kepler’s laws of planetary motion are three scientific laws describing the motion of planets around the Sun.
1- The orbit of ... more
The logit function is the inverse of the sigmoidal “logistic” function or logistic transform used in mathematics, especially in statistics. ... more
In finance, the net present value or net present worth of a time series of cash flows, both incoming and outgoing, is defined as the sum of the present ... more
An achromatic lens or achromat is a lens that is designed to limit the effects of chromatic and spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are corrected to ... more
In mathematics, generalised means are a family of functions for aggregating sets of numbers, that include as special cases the arithmetic, geometric, and ... more
A compound pendulum is a body formed from an assembly of particles or continuous shapes that rotates rigidly around a pivot. Its moments of inertia is the ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
The awe‐inspiring Great Pyramid of Cheops was built more than 4500 years ago. Its square base, originally 230 m on a side, covered 13.1 acres, and it was 146 m high (H), with a mass of about 7×10^9 kg. (The pyramid’s dimensions are slightly different today due to quarrying and some sagging). Historians estimate that 20,000 workers spent 20 years to construct it, working 12-hour days, 330 days per year.