Search results
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to ... more
In celestial mechanics, the mean anomaly is an angle used in calculating the position of a body in an elliptical orbit in the classical two-body problem. ... more
In mathematics, a magic cube is the 3-dimensional equivalent of a magic square, that is, a number of integers arranged in a n x n x n pattern such that the ... more
Capital market line (CML) is the tangent line drawn from the point of the risk-free asset to the feasible region for risky ... more
In probability theory, a conditional probability measures the probability of an event given that (by assumption, presumption, assertion or evidence) ... more
Is a predefined diametral position on the gear, where the circular tooth thickness, pressure angle and helix angles are defined. The standard pitch ... more
The Sortino ratio measures the risk-adjusted return of an investment asset, portfolio, or strategy. It is a modification of the Sharpe ratio but penalizes ... more
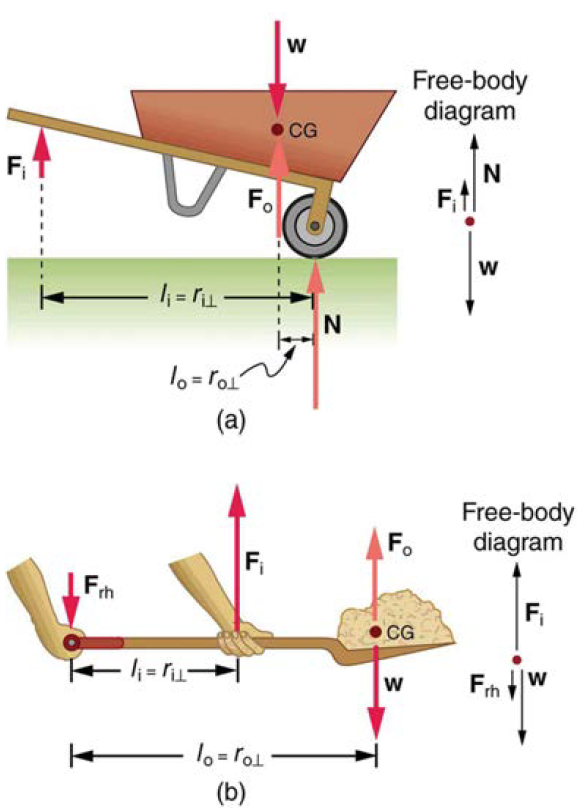
(a) In the case of the wheelbarrow, the output force or load is between the pivot and the input force. The pivot is the wheel’s axle. Here, the output force is greater than the input force. Thus, a wheelbarrow enables you to lift much heavier loads than you could with your body alone. (b) In the case of the shovel, the input force is between the pivot and the load, but the input lever arm is shorter than the output lever arm. The pivot is at the handle held by the right hand. Here, the output force (supporting the shovel’s load) is less than the input force (from the hand nearest the load), because the input is exerted closer to the pivot than is the output.
Strategy
Here, we use the concept of mechanical advantage.
Discussion
An even longer handle would reduce the force needed to lift the load. The MA here is:
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
In astrodynamics and aerospace, a delta-v budget is an estimate of the total delta-v required for a space mission. It is calculated as the sum of the ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
In the wheelbarrow of the following figure the load has a perpendicular lever arm of 7.50 cm, while the hands have a perpendicular lever arm of 1.02 m.(a) What upward force must you exert to support the wheelbarrow and its load if their combined mass is 45.0 kg? (b) What force does the wheelbarrow exert on the ground?