Search results
The cross section is an effective area that quantifies the intrinsic likelihood of a scattering event when an incident beam strikes a target object, made ... more
In geometry, Napoleon’s theorem states that if equilateral triangles are constructed on the sides of any triangle, either all outward, or all inward, ... more
A strain is a normalized measure of deformation representing the displacement between particles in the body relative to a reference length.The concept of ... more
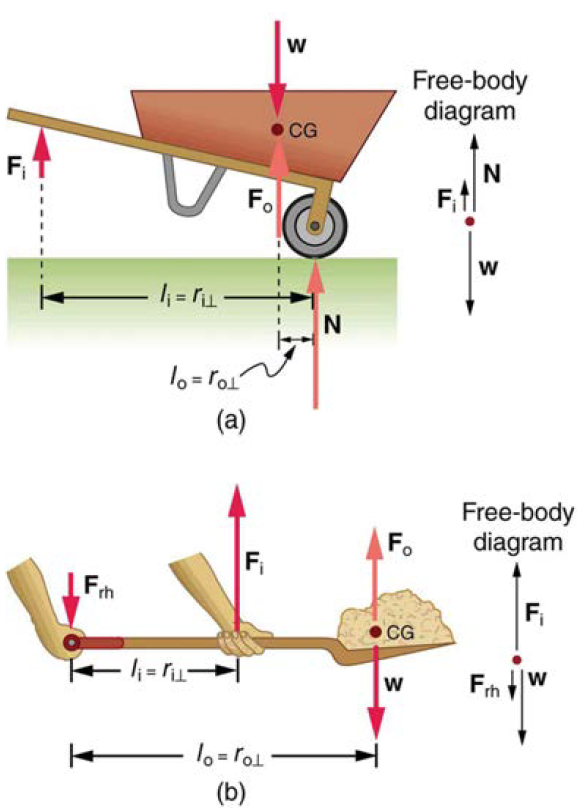
(a) In the case of the wheelbarrow, the output force or load is between the pivot and the input force. The pivot is the wheel’s axle. Here, the output force is greater than the input force. Thus, a wheelbarrow enables you to lift much heavier loads than you could with your body alone. (b) In the case of the shovel, the input force is between the pivot and the load, but the input lever arm is shorter than the output lever arm. The pivot is at the handle held by the right hand. Here, the output force (supporting the shovel’s load) is less than the input force (from the hand nearest the load), because the input is exerted closer to the pivot than is the output.
Strategy
Here, we use the concept of mechanical advantage.
Discussion
An even longer handle would reduce the force needed to lift the load. The MA here is:
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
In materials science, a general rule of mixtures is a weighted mean used to predict various properties of a composite material made up of continuous and ... more
In materials science, a general rule of mixtures is a weighted mean used to predict various properties of a composite material made up of continuous and ... more
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton’s second and third laws. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the ... more
Deformation in continuum mechanics is the transformation of a body from a reference configuration to a current configuration.
Strain is a normalized
... more
A solenoid is a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. In physics, the term refers specifically to a long, thin loop of wire, often wrapped around a ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
In the wheelbarrow of the following figure the load has a perpendicular lever arm of 7.50 cm, while the hands have a perpendicular lever arm of 1.02 m.(a) What upward force must you exert to support the wheelbarrow and its load if their combined mass is 45.0 kg? (b) What force does the wheelbarrow exert on the ground?