Search results
The Magnus effect is the commonly observed effect in which a spinning ball (or cylinder) curves away from its principal flight path.The overall behaviour ... more
Formula first contributed by:
zfyl
The R-value is a measure of thermal resistance, or ability of heat to transfer from hot ... more
The wetted perimeter is the perimeter of the cross sectional area that is “wet”. The term wetted perimeter is common in civil engineering, ... more
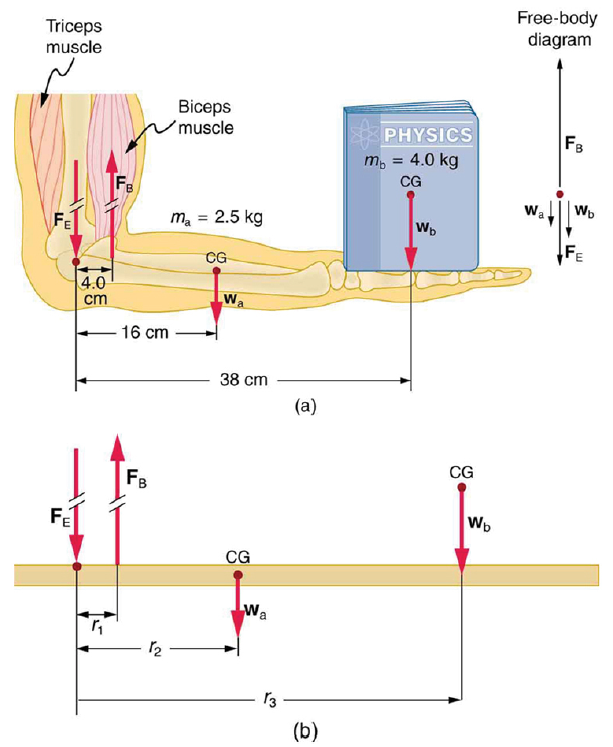
(a) The figure shows the forearm of a person holding a book. The biceps exert a force FB to support the weight of the forearm and the book. The triceps are assumed to be relaxed. (b) Here, you can view an approximately equivalent mechanical system with the pivot at the elbow joint
Strategy
There are four forces acting on the forearm and its load (the system of interest). The magnitude of the force of the biceps is FB, that of the elbow joint is FE, that of the weights of the forearm is wa , and its load is wb. Two of these are unknown FB, so that the first condition for equilibrium cannot by itself yield FB . But if we use the second condition and choose the pivot to be at the elbow, then the torque due to FE is zero, and the only unknown becomes FB .
Solution
The torques created by the weights are clockwise relative to the pivot, while the torque created by the biceps is counterclockwise; thus, the second condition for equilibrium (net τ = 0) becomes
Note that sin θ = 1 for all forces, since θ = 90º for all forces. This equation can easily be solved for FB in terms of known quantities,yielding. Entering the known values gives
which yields
Now, the combined weight of the arm and its load is known, so that the ratio of the force exerted by the biceps to the total weight is
Discussion
This means that the biceps muscle is exerting a force 7.38 times the weight supported.
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Blood alcohol content (BAC), also called blood alcohol concentration, blood ethanol concentration, or blood alcohol level is most ... more
The Stokes number (Stk), named after George Gabriel Stokes, is a dimensionless number corresponding to the behavior of particles suspended in a fluid flow. ... more
The Shields parameter, also called the Shields criterion or Shields number, is a nondimensional number used to calculate the initiation of motion of ... more
The Earth Similarity Index, ESI or “easy scale” is a measure of how physically similar a planetary-mass object is to ... more
A ball screw is a mechanical linear actuator that translates rotational motion to linear motion with little friction. A threaded shaft provides a helical ... more
The Heronian mean of two non-negative real numbers is a weighted mean of their arithmetic and geometric means.The weighted mean is similar to an ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
Calculate the force the biceps muscle must exert to hold the forearm and its load as shown in the figure below, and compare this force with the weight of the forearm plus its load. You may take the data in the figure to be accurate to three significant figures.