Search results
TAS can be calculated as a function of Mach number and static air temperature. Combining the TAS for ... more
Capillary action (sometimes capillarity, capillary motion, or wicking) is the ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of, and ... more
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force ... more
A leadscrew (or lead screw), also known as a power screw or translation screw, is a screw used as a linkage in a machine, to translate turning motion into ... more
Drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) refers to forces acting ... more
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force ... more
Energy–maneuverability theory is a model of aircraft performance. It was developed by Col. John Boyd, and is useful in describing an aircraft’s ... more
The gravity of Earth, which is denoted by g, refers to the acceleration that the Earth imparts to objects on or near its surface due to gravity. In SI ... more
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton’s second and third laws. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the ... more
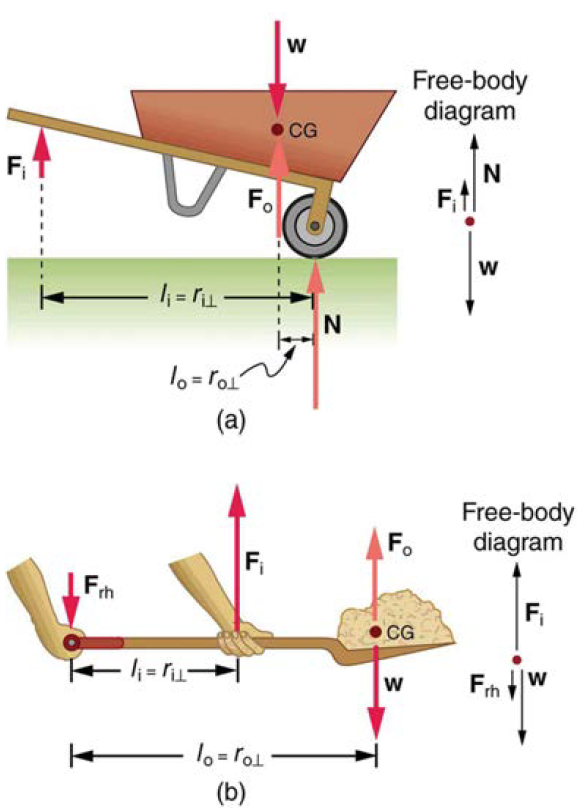
(a) In the case of the wheelbarrow, the output force or load is between the pivot and the input force. The pivot is the wheel’s axle. Here, the output force is greater than the input force. Thus, a wheelbarrow enables you to lift much heavier loads than you could with your body alone. (b) In the case of the shovel, the input force is between the pivot and the load, but the input lever arm is shorter than the output lever arm. The pivot is at the handle held by the right hand. Here, the output force (supporting the shovel’s load) is less than the input force (from the hand nearest the load), because the input is exerted closer to the pivot than is the output.
Strategy
Here, we use the concept of mechanical advantage.
Discussion
An even longer handle would reduce the force needed to lift the load. The MA here is:
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
In the wheelbarrow of the following figure the load has a perpendicular lever arm of 7.50 cm, while the hands have a perpendicular lever arm of 1.02 m.(a) What upward force must you exert to support the wheelbarrow and its load if their combined mass is 45.0 kg? (b) What force does the wheelbarrow exert on the ground?