Search results
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a ... more
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.The kinetic energy of a point object (an object so small that its mass ... more
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a ... more
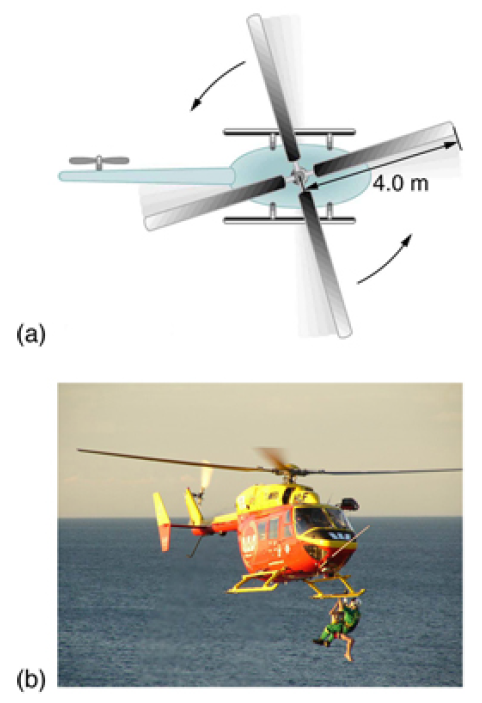
The first image shows how helicopters store large amounts of rotational kinetic energy in their blades. This energy must be put into the blades before takeoff and maintained until the end of the flight. The engines do not have enough power to simultaneously provide lift and put significant rotational energy into the blades.
The second image shows a helicopter from the Auckland Westpac Rescue Helicopter Service. Over 50,000 lives have been saved since its operations beginning in 1973. Here, a water rescue operation is shown. (credit: 111 Emergency, Flickr)
Strategy
Rotational and translational kinetic energies can be calculated from their definitions. The last part of the problem relates to the idea that energy can change form, in this case from rotational kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy.
Solution for (a)
We must convert the angular velocity to radians per second and calculate the moment of inertia before we can find Er . The angular velocity ω for 1 r.p.m is
and for 300 r.p.m
The moment of inertia of one blade will be that of a thin rod rotated about its end.
The total I is four times this moment of inertia, because there are four blades. Thus,
and so The rotational kinetic energy is
Solution for (b)
Translational kinetic energy is defined as
To compare kinetic energies, we take the ratio of translational kinetic energy to rotational kinetic energy. This ratio is
Solution for (c)
At the maximum height, all rotational kinetic energy will have been converted to gravitational energy. To find this height, we equate those two energies:
Discussion
The ratio of translational energy to rotational kinetic energy is only 0.380. This ratio tells us that most of the kinetic energy of the helicopter is in its spinning blades—something you probably would not suspect. The 53.7 m height to which the helicopter could be raised with the rotational kinetic energy is also impressive, again emphasizing the amount of rotational kinetic energy in the blades.
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
An elastic collision is an encounter between two bodies in which the total kinetic energy of the two bodies after the encounter is equal to their total ... more
An elastic collision is an encounter between two bodies in which the total kinetic energy of the two bodies after the encounter is equal to their total ... more
A flywheel is a rotating mechanical device that is used to store rotational energy. Flywheel energy storage works by accelerating a rotor to a very high ... more
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. Space propulsion or in-space propulsion exclusively deals with ... more
Escape velocity is the speed at which the kinetic energy plus the gravitational potential energy of an object is zero. It is the speed needed to ... more
In the gravitational two-body problem, the specific orbital energy (or vis-viva energy) of two orbiting bodies is the constant sum of their mutual ... more
In astrodynamics, the vis viva equation, also referred to as orbital energy conservation equation, is one of the fundamental equations that govern the ... more
Due to the self-induction effect, electrostatic energy behaves as having some sort of momentum and “apparent” electromagnetic mass, which can increase the ... more
Due to the self-induction effect, electrostatic energy behaves as having some sort of momentum and “apparent” electromagnetic mass, which can ... more
In physics, mass–energy equivalence is the concept that the mass of an object or system is a measure of its energy content. A physical system has a ... more
The rotational energy or angular kinetic energy is the kinetic energy due to the rotation of an object and is part of its total kinetic energy. The ... more
In physics, the energy–momentum relation, or relativistic dispersion relation, is the relativistic equation relating any object’s rest (intrinsic) ... more
In astrodynamics, the vis viva equation, also referred to as orbital energy conservation equation, is one of the fundamental equations that govern the ... more
Radiation pressure is the pressure exerted upon any surface exposed to electromagnetic radiation. Radiation pressure implies an interaction between ... more
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to produce electrical power, windmills for mechanical ... more
The orbital speed of a body, generally a planet, a natural satellite, an artificial satellite, or a multiple star, is the speed at which it orbits around ... more
In astrodynamics, the vis viva equation, also referred to as orbital energy conservation equation, is one of the fundamental equations that govern the ... more
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed.
Total energy is constant in any process. It may change in form or be transferred from one system to
... more
The orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect ... more
The orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect ... more
Thermal energy is a term sometimes used to refer to the internal energy present in a system in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium by virtue of its ... more
Shear stress, is defined as the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. Shear stress arises from the force vector component parallel to ... more
Joule heating , is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor releases heat. Joule heating is depending on the resistance ... more
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to produce electrical power, windmills for mechanical ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
A typical small rescue helicopter, like the one in the Figure below, has four blades, each is 4.00 m long and has a mass of 50.0 kg. The blades can be approximated as thin rods that rotate about one end of an axis perpendicular to their length. The helicopter has a total loaded mass of 1000 kg. (a) Calculate the rotational kinetic energy in the blades when they rotate at 300 rpm. (b) Calculate the translational kinetic energy of the helicopter when it flies at 20.0 m/s, and compare it with the rotational energy in the blades. (c) To what height could the helicopter be raised if all of the rotational kinetic energy could be used to lift it?