Search results
The dynamic (shear) viscosity of a fluid expresses its resistance to shearing flows, where adjacent layers move parallel to each other with different ... more
In mechanics, a cylinder stress is a stress distribution with rotational symmetry; that is, which remains unchanged if the stressed object is rotated about ... more
A compound machine is a machine formed from a set of simple machines connected in series with the output force of one providing the input force to the ... more
Torque, moment or moment of force (see the terminology below) is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis. In addition to the tendency to ... more
A photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic ... more
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. Ideally, the device preserves ... more
In materials science, shear modulus or modulus of rigidity, denoted by G, or sometimes S or μ, is defined as the ratio of shear stress to the shear strain. ... more
The electric field is a component of the electromagnetic field. It is a vector field, and it is generated by electric charges or time-varying magnetic ... more
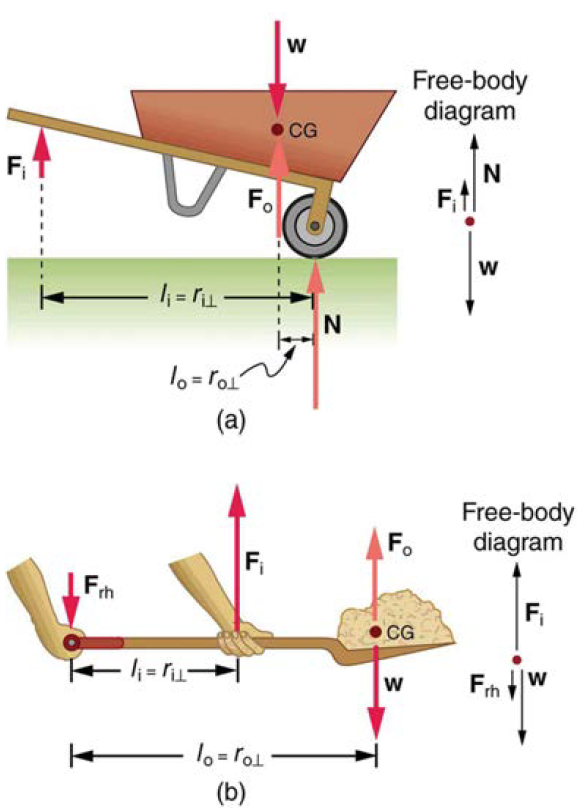
(a) In the case of the wheelbarrow, the output force or load is between the pivot and the input force. The pivot is the wheel’s axle. Here, the output force is greater than the input force. Thus, a wheelbarrow enables you to lift much heavier loads than you could with your body alone. (b) In the case of the shovel, the input force is between the pivot and the load, but the input lever arm is shorter than the output lever arm. The pivot is at the handle held by the right hand. Here, the output force (supporting the shovel’s load) is less than the input force (from the hand nearest the load), because the input is exerted closer to the pivot than is the output.
Strategy
Here, we use the concept of mechanical advantage.
Discussion
An even longer handle would reduce the force needed to lift the load. The MA here is:
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
In the wheelbarrow of the following figure the load has a perpendicular lever arm of 7.50 cm, while the hands have a perpendicular lever arm of 1.02 m.(a) What upward force must you exert to support the wheelbarrow and its load if their combined mass is 45.0 kg? (b) What force does the wheelbarrow exert on the ground?