Search results
f is the number of sheaves in the purchase, and there is a roughly % loss of efficiency at each sheave due to friction, then:
... more
A block and tackle is a system of two or more pulleys with a rope or cable threaded between them, usually used to lift or pull heavy loads.The formula used ... more
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. Ideally, the device preserves ... more
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. Ideally, the device preserves ... more
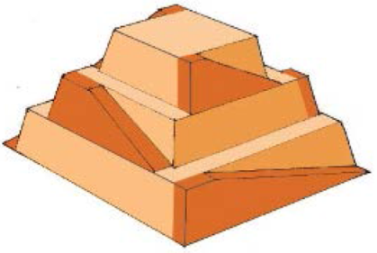
a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the pyramid, given its center of mass is at one-fourth its height.
b) Only a fraction of the workers lifted blocks; most were involved in support services such as building ramps, bringing food and water, and hauling blocks to the site. Calculate the efficiency of the workers who did the lifting, assuming there were 1000 of them and they consumed food energy at the rate of 300 Kcal/hour.
first we calculate the number of hours worked per year.
then we calculate the number of hours worked in the 20 years.
Then we calculate the energy consumed in 20 years knowing the energy consumed per hour and the total hours worked in 20 years.
The efficiency is the resulting potential energy divided by the consumed energy.
As used in mechanical engineering, the term tractive force can either refer to the total traction a vehicle exerts on a surface, or the amount of the total ... more
Engine displacement is the volume swept by all the pistons inside the cylinders of a reciprocating engine in a single movement from top dead centre (... more
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. Ideally, the device preserves ... more
In thermodynamics, an isentropic process is an idealized thermodynamic process that is adiabatic and in which the work transfers of the system are ... more
In thermodynamics, an isentropic process is an idealized thermodynamic process that is adiabatic and in which the work transfers of the system are ... more
In thermodynamics, an isentropic process is an idealized thermodynamic process that is adiabatic and in which the work transfers of the system are ... more
As used in mechanical engineering, the term tractive force can either refer to the total traction a vehicle exerts on a surface, or the amount of the total ... more
In thermodynamics, an isentropic process is an idealized thermodynamic process that is adiabatic and in which the work transfers of the system are ... more
In thermodynamics, an isentropic process is an idealized thermodynamic process that is adiabatic and in which the work transfers of the system are ... more
Metcalfe’s law states that the value of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected users of the system ... more
Damped harmonic motion is a real oscillation, in which an object is hanging on a spring. Because of the existence of internal friction and air resistance, ... more
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. Ideally, the device preserves ... more
The power imparted into a fluid increases the energy of the fluid per unit volume. Thus the power relationship is between the conversion of the mechanical ... more
In mechanical engineering, backlash, sometimes called lash or play, is clearance or lost motion in a mechanism caused by gaps between the parts. It can be ... more
In mechanical engineering, backlash, sometimes called lash or play, is clearance or lost motion in a mechanism caused by gaps between the parts. It can be ... more
A simple machine is a mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. In general, they can be defined as the simplest mechanisms that ... more
A Bingham plastic is a viscoplastic material that behaves as a rigid body at low stresses but flows as a viscous fluid at high stress. It is named after ... more
In fluid flow, friction loss (or skin friction) is the loss of pressure or “head” that occurs in pipe or duct flow due to the effect of the fluid’s ... more
The equation for the desired radius of a curve, takes into account the factors of speed and superelevation (e). This equation can be algebraically ... more
A ball screw is a mechanical linear actuator that translates rotational motion to linear motion with little friction. A threaded shaft provides a helical ... more
The Knoop hardness test /kəˈnuːp/ is a microhardness test – a test for mechanical hardness used particularly for very brittle materials or thin sheets, ... more
A regenerative brake is an energy recovery mechanism which slows a vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form which can be either used ... more
A Bingham plastic is a viscoplastic material that behaves as a rigid body at low stresses but flows as a viscous fluid at high stress. It is named after ... more
A Bingham plastic is a viscoplastic material that behaves as a rigid body at low stresses but flows as a viscous fluid at high stress. It is named after ... more
An exact description of friction loss (Darcy Weisbach equation) for Bingham plastics in fully developed laminar pipe flow was first published by ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
The awe‐inspiring Great Pyramid of Cheops was built more than 4500 years ago. Its square base, originally 230 m on a side, covered 13.1 acres, and it was 146 m high (H), with a mass of about 7×10^9 kg. (The pyramid’s dimensions are slightly different today due to quarrying and some sagging). Historians estimate that 20,000 workers spent 20 years to construct it, working 12-hour days, 330 days per year.