Search results
A harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force, proportional to the displacement. If a ... more
Centrifugal pumps are a sub-class of dynamic axis-symmetric work-absorbing turbo-machinery.The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric ... more
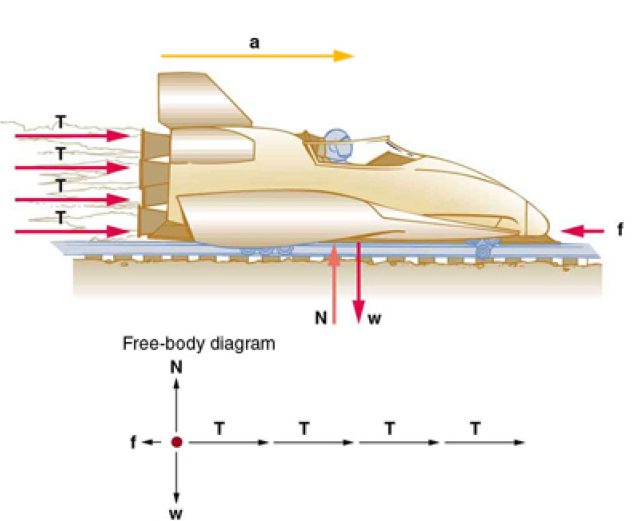
A sled experiences a rocket thrust that accelerates it to the right.Each rocket creates an identical thrust T . As in other situations where there is only horizontal acceleration, the vertical forces cancel. The ground exerts an upward force N on the system that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to its weight,w.The system here is the sled, its rockets, and rider, so none of the forces between these objects are considered. The arrow representing friction ( f ) is drawn larger than scale.
Assumptions: The mass of the Sled remains steady throughout the operation
Strategy
Although there are forces acting vertically and horizontally, we assume the vertical forces cancel since there is no vertical acceleration. This leaves us with only horizontal forces and a simpler one-dimensional problem. Directions are indicated with plus or minus signs, with right taken as the positive direction. See the free-body diagram in the figure.
Solution
Since acceleration, mass, and the force of friction are given, we start with Newton’s second law and look for ways to find the thrust of the engines. Since we have defined the direction of the force and acceleration as acting “to the right,” we need to consider only the magnitudes of these quantities in the calculations. Hence we begin with
Fnet is the net force along the horizontal direction, m is the rocket’s mass and a the acceleration.
We can see from the Figure at the top, that the engine thrusts add, while friction opposes the thrust.
Tt is the total thrust from the 4 rockets, Fnet the net force along the horizontal direction and Ff the force of friction.
Finally, since there are 4 rockets, we calculate the thrust that each one provides:
T is the individual Thrust of each engine, b is the number of rocket engines
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
A banked turn (aka. banking turn) is a turn or change of direction in which the vehicle banks or inclines, usually towards the inside of the turn. For a ... more
A ball screw is a mechanical linear actuator that translates rotational motion to linear motion with little friction. A threaded shaft provides a helical ... more
In fluid mechanics, the Roshko number is a dimensionless number describing oscillating flow mechanisms.It is related to the Strouhal number and the ... more
The Froessling equation is a specific correlation of the Sherwood number (Sh) for a single sphere analysis.
... more
In geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. The bearing capacity of soil is the ... more
In geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. The bearing capacity of soil is the ... more
In geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. The bearing capacity of soil is the ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
Prior to manned space flights, rocket sleds were used to test aircraft, missile equipment, and physiological effects on human subjects at high speeds. They consisted of a platform that was mounted on one or two rails and propelled by several rockets. Calculate the magnitude of force exerted by each rocket, called its thrust T , for the four-rocket propulsion system shown in the Figure below. The sled’s initial acceleration is 49 m/s 2, the mass of the system is 2100 kg, and the force of friction opposing the motion is known to be 650 N.