Search results
In celestial mechanics, the mean anomaly is an angle used in calculating the position of a body in an elliptical orbit in the classical two-body problem. ... more
Nodal precession is the precession of an orbital plane around the rotation axis of an astronomical body such as Earth. This precession is due to the ... more
Escape velocity is the speed at which the kinetic energy plus the gravitational potential energy of an object is zero. It is the speed needed to ... more
In astronomy, Kepler’s laws of planetary motion are three scientific laws describing the motion of planets around the Sun.
1- The orbit of ... more
The free-fall time is the characteristic time that would take a body to collapse under its own gravitational attraction, if no other forces existed to ... more
The free-fall time is the characteristic time that would take a body to collapse under its own gravitational attraction, if no other forces existed to ... more
In celestial mechanics, true anomaly is an angular parameter that defines the position of a body moving along a Keplerian orbit. It is the angle between ... more
The Schwarzschild radius (sometimes historically referred to as the gravitational radius) is the radius of a sphere such that, if all the ... more
In physics, the ballistic trajectory of a projectile is the path that a thrown or launched projectile or missile without propulsion will take under the ... more
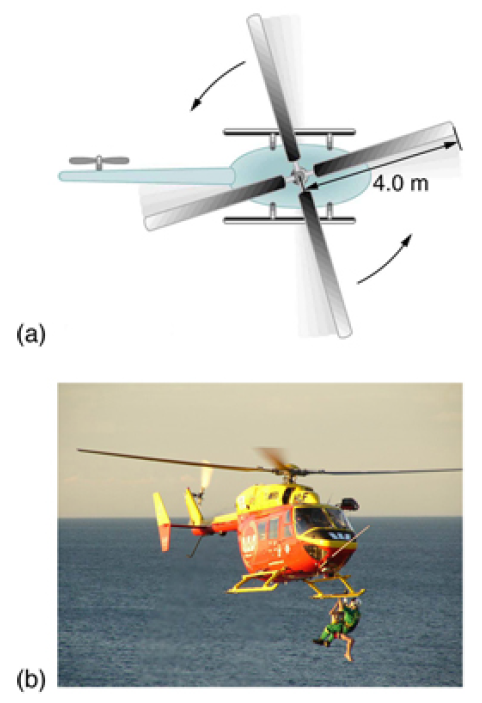
The first image shows how helicopters store large amounts of rotational kinetic energy in their blades. This energy must be put into the blades before takeoff and maintained until the end of the flight. The engines do not have enough power to simultaneously provide lift and put significant rotational energy into the blades.
The second image shows a helicopter from the Auckland Westpac Rescue Helicopter Service. Over 50,000 lives have been saved since its operations beginning in 1973. Here, a water rescue operation is shown. (credit: 111 Emergency, Flickr)
Strategy
Rotational and translational kinetic energies can be calculated from their definitions. The last part of the problem relates to the idea that energy can change form, in this case from rotational kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy.
Solution for (a)
We must convert the angular velocity to radians per second and calculate the moment of inertia before we can find Er . The angular velocity ω for 1 r.p.m is
and for 300 r.p.m
The moment of inertia of one blade will be that of a thin rod rotated about its end.
The total I is four times this moment of inertia, because there are four blades. Thus,
and so The rotational kinetic energy is
Solution for (b)
Translational kinetic energy is defined as
To compare kinetic energies, we take the ratio of translational kinetic energy to rotational kinetic energy. This ratio is
Solution for (c)
At the maximum height, all rotational kinetic energy will have been converted to gravitational energy. To find this height, we equate those two energies:
Discussion
The ratio of translational energy to rotational kinetic energy is only 0.380. This ratio tells us that most of the kinetic energy of the helicopter is in its spinning blades—something you probably would not suspect. The 53.7 m height to which the helicopter could be raised with the rotational kinetic energy is also impressive, again emphasizing the amount of rotational kinetic energy in the blades.
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
A typical small rescue helicopter, like the one in the Figure below, has four blades, each is 4.00 m long and has a mass of 50.0 kg. The blades can be approximated as thin rods that rotate about one end of an axis perpendicular to their length. The helicopter has a total loaded mass of 1000 kg. (a) Calculate the rotational kinetic energy in the blades when they rotate at 300 rpm. (b) Calculate the translational kinetic energy of the helicopter when it flies at 20.0 m/s, and compare it with the rotational energy in the blades. (c) To what height could the helicopter be raised if all of the rotational kinetic energy could be used to lift it?