Search results
Mean time between failures (MTBF) is the predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a system during operation. ... more
Earnings per share is the monetary value of earnings per each outstanding share of a company’s common stock. In business, net income – also ... more
In financial accounting, an asset is an economic resource. Anything tangible or intangible that is capable of being owned or controlled to produce value ... more
n financial accounting, an asset is an economic resource. Anything tangible or intangible that is capable of being owned or controlled to produce value and ... more
where t is the total consumption time, td is the days of consumption and th the hours of consumption per day
where P is Power consumption rate, E is the energy supplied by the electricity company and t is consumption time
keywords:
ballistics
where C is the total cost and CkW is the cost per kilowatt hour
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Earned value management (EVM), earned value project management, or earned value performance management (... more
Earned value management (EVM), earned value project management, or earned value performance management (... more
Earned value management (EVM), earned value project management, or earned value performance management (... more
Solar rotation is able to vary with latitude because the Sun is composed of a gaseous plasma. The rate of rotation is observed to be fastest at the equator ... more
Electric power is the rate, per unit time, at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule ... more
The weighted average cost of capital is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets. It is the ... more
In finance, holding period return (HPR) is the total return on an asset or portfolio over the period during which it was held. It ... more
The position of the Sun in the sky is a function of both time and the geographic coordinates of the observer on the surface of the Earth. As the Earth ... more
The position of the Sun in the sky is a function of both time and the geographic coordinates of the observer on the surface of the Earth. As the Earth ... more
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution (French pronunciation [pwasɔ̃]; in English usually /ˈpwɑːsɒn/), named after French ... more
Earned value management (EVM), earned value project management, or earned value performance management (... more
Earned value management (EVM), earned value project management, or earned value performance management (... more
Dermott’s law is an empirical formula for the orbital period of major satellites orbiting planets in the Solar System. It was identified by the ... more
The modulus of elasticity of concrete is a function of the modulus of elasticity of the aggregates and the cement matrix and their relative proportions. ... more
Total Shareholder Return (TSR) (or simply Total Return) is a measure of the performance of different companies’ stocks and shares ... more
The modulus of elasticity of concrete is a function of the modulus of elasticity of the aggregates and the cement matrix and their relative proportions. ... more
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an orbit around the Earth with an orbital period of one sidereal day ... more
Estimate how long it will take to complete a work by two people, from their individual working capacities.
... more
Trip distribution (or destination choice or zonal interchange analysis) is the second component (after trip generation, but before mode choice and route ... more
Rule of 72 is a method for estimating an investment’s doubling time. The rule number 72 is divided by the interest percentage per period to obtain ... more
The quantity theory of money, says that any change in the amount of money in a system will change the price level. The equation of exchange is the ... more
Concrete has relatively high compressive strength, but significantly lower tensile strength. As a result, without compensating, concrete would almost ... more
Purchasing power (sometimes retroactively called adjusted for inflation) is the number of goods or services that can be purchased with a unit of currency. ... more
In orbital mechanics, mean motion (represented by ) is a measure of how fast a satellite progresses around its elliptical orbit. The mean motion is the ... more
The awe‐inspiring Great Pyramid of Cheops was built more than 4500 years ago. Its square base, originally 230 m on a side, covered 13.1 acres, and it was 146 m high (H), with a mass of about 7×10^9 kg. (The pyramid’s dimensions are slightly different today due to quarrying and some sagging). Historians estimate that 20,000 workers spent 20 years to construct it, working 12-hour days, 330 days per year.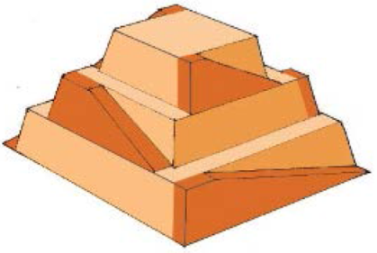
a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the pyramid, given its center of mass is at one-fourth its height.
b) Only a fraction of the workers lifted blocks; most were involved in support services such as building ramps, bringing food and water, and hauling blocks to the site. Calculate the efficiency of the workers who did the lifting, assuming there were 1000 of them and they consumed food energy at the rate of 300 Kcal/hour.
first we calculate the number of hours worked per year.
then we calculate the number of hours worked in the 20 years.
Then we calculate the energy consumed in 20 years knowing the energy consumed per hour and the total hours worked in 20 years.
The efficiency is the resulting potential energy divided by the consumed energy.
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
What is the cost of running a 0.600-kW computer 6.00 h per day for 30.0 d if the cost of electricity is $0.120 per kW ⋅ h ?