Search results
In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of energy emitted by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object per unit time. It is related to the ... more
In statistics, a likelihood ratio test is a statistical test used to compare the fit of two models, one of which (the null model) is a special case of the ... more
n financial accounting, an asset is an economic resource. Anything tangible or intangible that is capable of being owned or controlled to produce value and ... more
Log-normal (or lognormal) distribution is a continuous probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normally distributed. The standard ... more
Formula first contributed by:
trooper
In engineering, the damping ratio is a dimensionless measure describing how ... more
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an orbit around the Earth with an orbital period of one sidereal day ... more
Earnings per share is the monetary value of earnings per each outstanding share of a company’s common stock. Shares outstanding are all the shares of a ... more
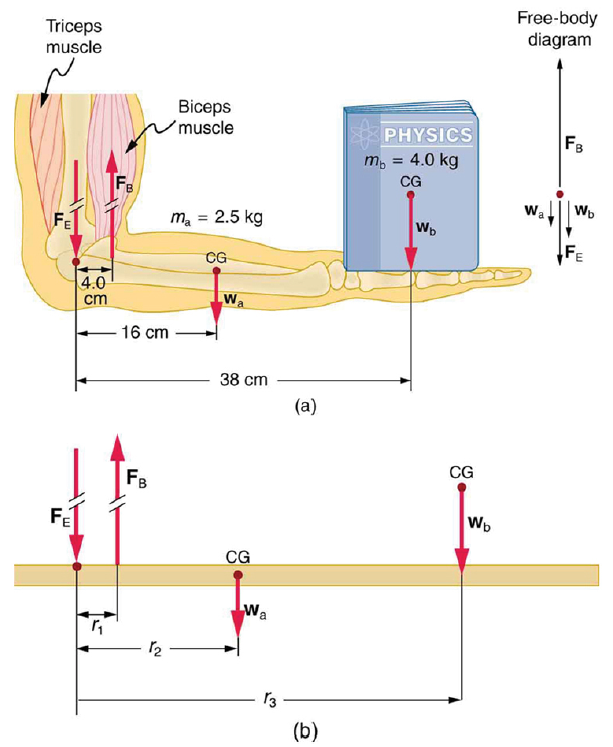
(a) The figure shows the forearm of a person holding a book. The biceps exert a force FB to support the weight of the forearm and the book. The triceps are assumed to be relaxed. (b) Here, you can view an approximately equivalent mechanical system with the pivot at the elbow joint
Strategy
There are four forces acting on the forearm and its load (the system of interest). The magnitude of the force of the biceps is FB, that of the elbow joint is FE, that of the weights of the forearm is wa , and its load is wb. Two of these are unknown FB, so that the first condition for equilibrium cannot by itself yield FB . But if we use the second condition and choose the pivot to be at the elbow, then the torque due to FE is zero, and the only unknown becomes FB .
Solution
The torques created by the weights are clockwise relative to the pivot, while the torque created by the biceps is counterclockwise; thus, the second condition for equilibrium (net τ = 0) becomes
Note that sin θ = 1 for all forces, since θ = 90º for all forces. This equation can easily be solved for FB in terms of known quantities,yielding. Entering the known values gives
which yields
Now, the combined weight of the arm and its load is known, so that the ratio of the force exerted by the biceps to the total weight is
Discussion
This means that the biceps muscle is exerting a force 7.38 times the weight supported.
Reference : OpenStax College,College Physics. OpenStax College. 21 June 2012.
http://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Creative Commons License : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
The weighted average cost of capital is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets. It is the ... more
...can't find what you're looking for?
Create a new formula
Calculate the force the biceps muscle must exert to hold the forearm and its load as shown in the figure below, and compare this force with the weight of the forearm plus its load. You may take the data in the figure to be accurate to three significant figures.